MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small (~22 nucleotides) non-coding RNA that regulate gene expression by binding to a specific messenger RNA (mRNA) and promoting its degradation. Since the first discovery of miRNA in Caenorhabditis elegans, studies have proven that miRNAs exist in almost all organisms. The human genome alone contains over 1,000 miRNAs, with a single miRNA capable of regulating hundreds of mRNA transcripts. Thus, a delicate balance between miRNA expression patterns and mRNA transcripts is crucial for healthy biological functions. Abnormal miRNA expression patterns are associated with several conditions, including various cancer types and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s Disease. As a result, miRNA expression profiling has become a valuable technique for identifying miRNA biomarkers associated with specific diseases.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has become an effective method for miRNA profiling, allowing researchers to discover novel miRNAs and evaluate the expression levels of known ones in a single experiment. Despite its benefits, establishing an NGS-based workflow for miRNA profiling can be challenging due to its multistep process. The typical workflow includes sample collection, RNA isolation, miRNA library preparation, sequencing, and data analysis. Each step has the potential to introduce biases that may impact the accuracy of miRNA detection. Researchers must carefully strategize each step to fully leverage the capabilities of NGS for miRNA analysis.
This guide outlines essential steps and key considerations required to establish a robust workflow for accurate miRNA expression profiling using NGS technologies.
-
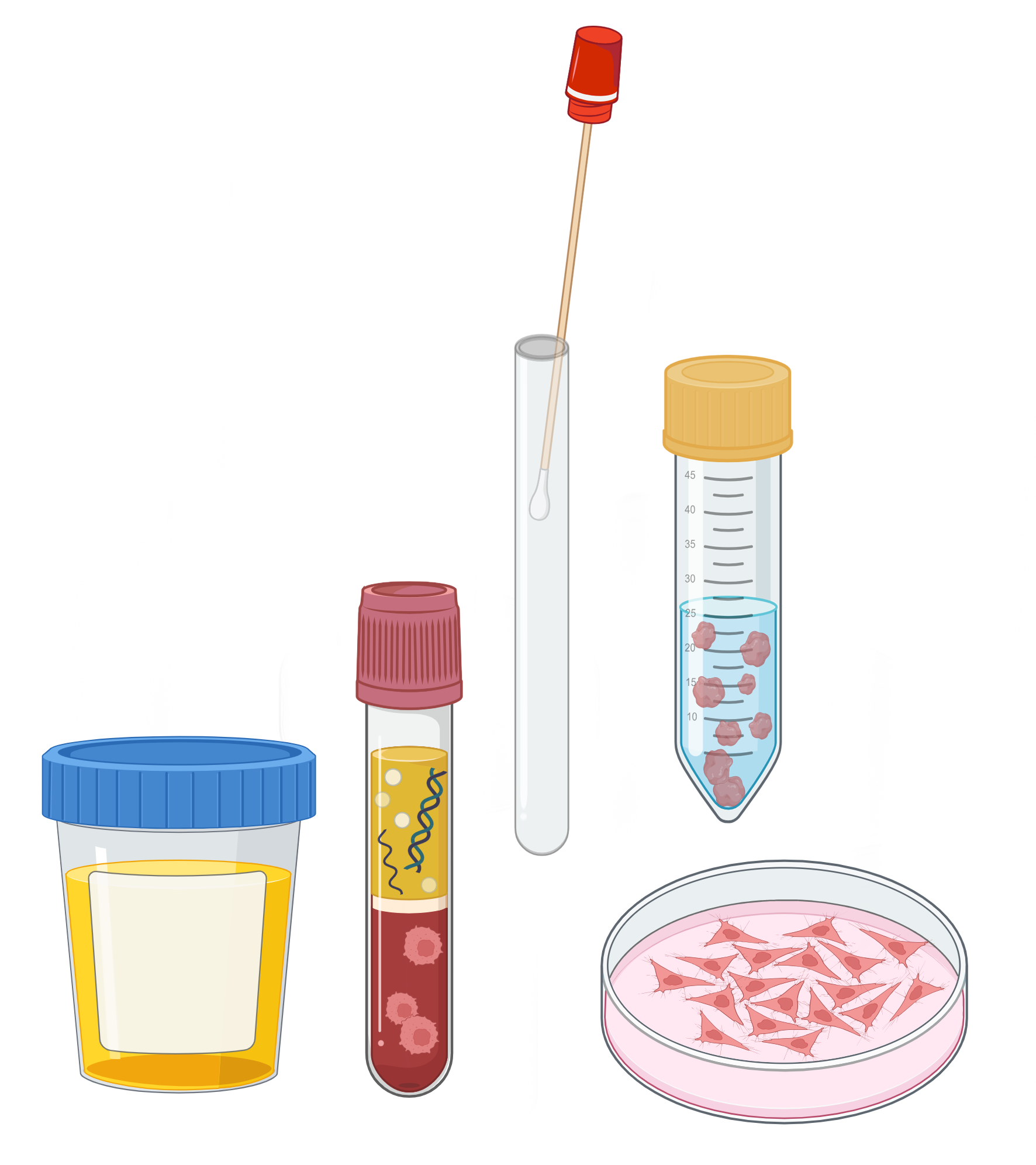
Sample Collection
RNA profiles can change within minutes of sample collection. Stabilizing reagents such as DNA/RNA Shield™ will protect and maintain the integrity of small RNA profiles even at room temperature
-
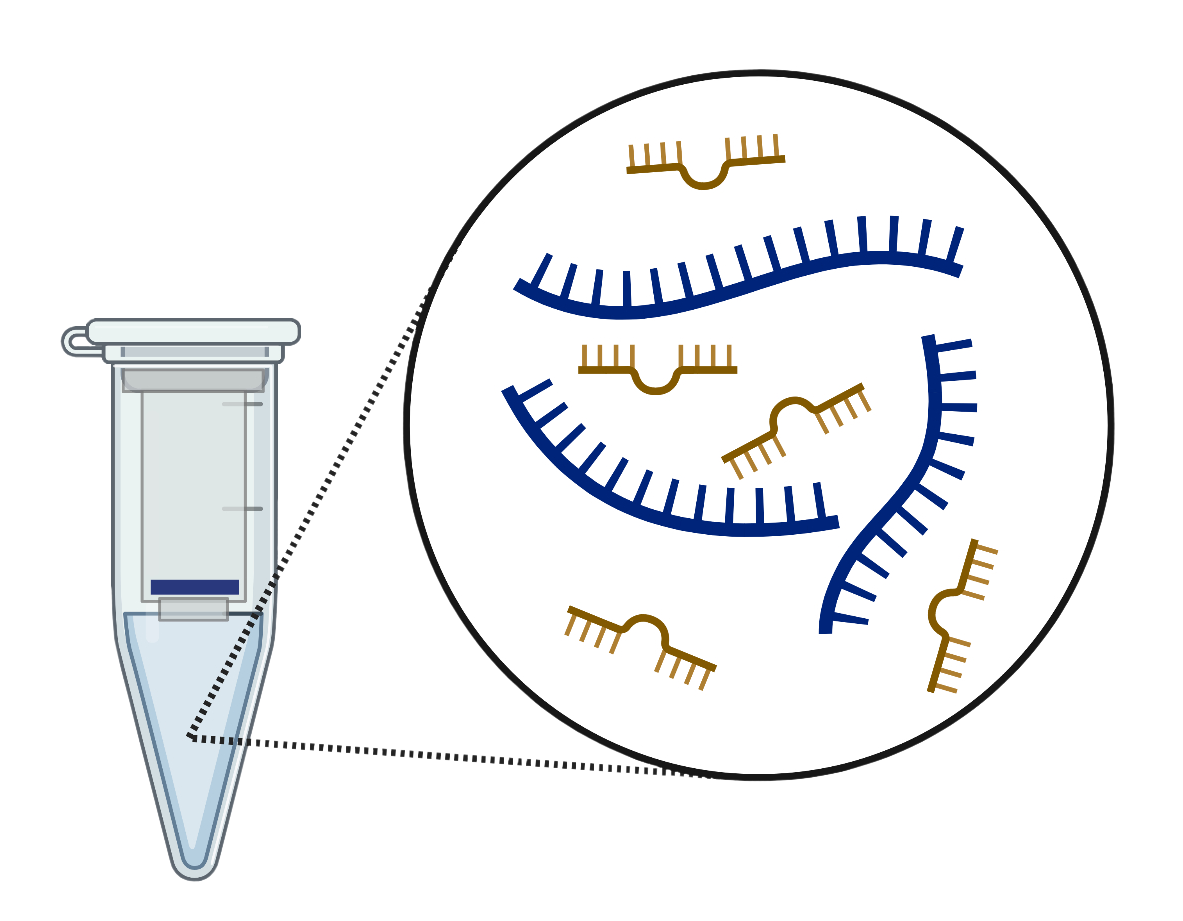
RNA Isolation
Many methods of RNA isolation do not adequately purify small RNAs, resulting in incomplete expression profiles. To obtain reliable data, it is critical that the RNA purification method effectively removes contaminants and retains small RNAs from samples.
-
Library Preparation
The process of generating miRNA libraries involves multiple steps that can introduce bias and produce inaccurate data. Zymo Research RNA-Seq Services utilizes an optimized protocol to increase reproducibility and enable accurate small RNA biomarker discovery.
-
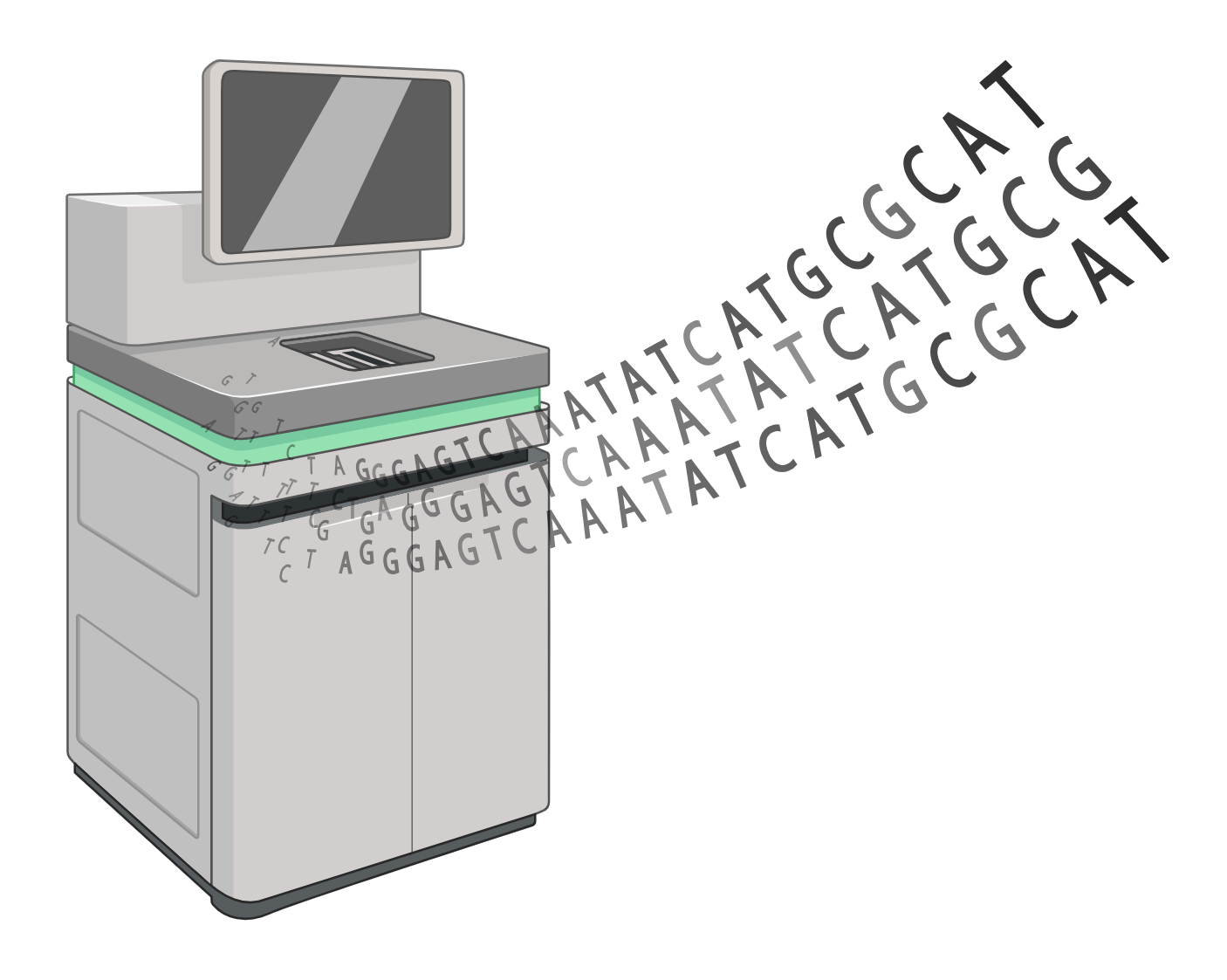
Quality Control and Sequencing
Ensure optimal sequencing performance by confirming the presence and concentration of miRNA libraries. Visualize the size of the library with an automated electrophoresis system and quantify the yield with a qPCR-based assay.
-

Data Analysis
NGS generates large amounts of data, making quality control essential. Removing low-quality bases via steps such as trimming helps avoid errors caused by technical issues and supports accurate biomarker discoveries.
