Simplify the Preparation of Transfection-Grade Plasmid DNA
ZymoPURE Endotoxin-Free Plasmid Purification Kits
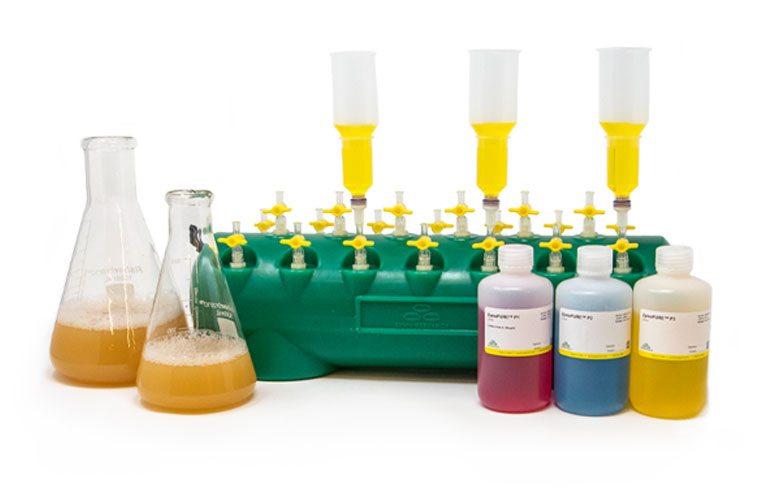
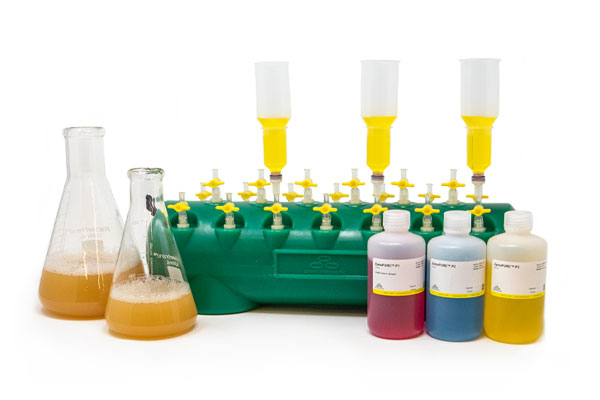
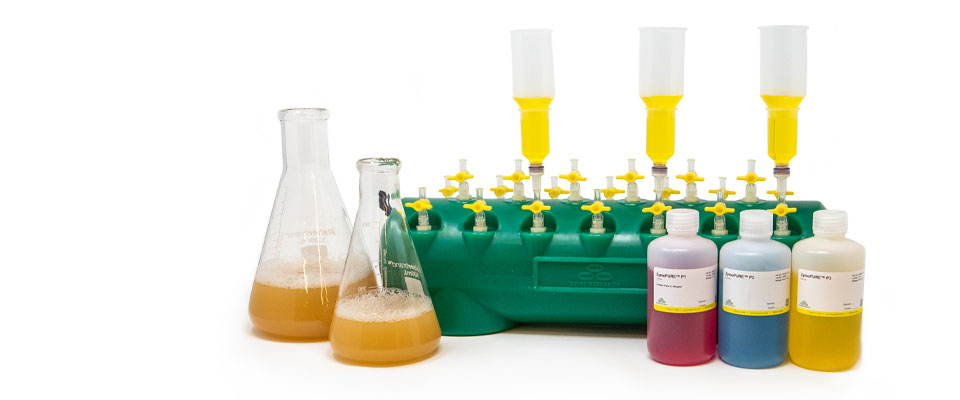



Ultra-Fast Midi & Maxipreps

Fastest
Simple 16-minute Midi/Maxi preps
Highest Yield
Up to 25 mg from a spin-column

Ultra-Pure
Endotoxin-Free & Transfection Ready
Endotoxin-Free Plasmid Purification Reinvented
Save more than 2 hours per prep!
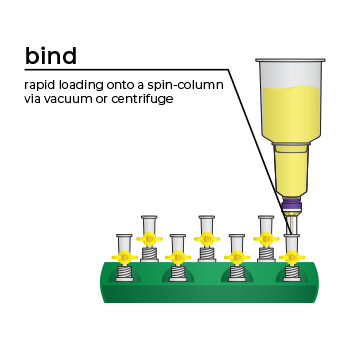
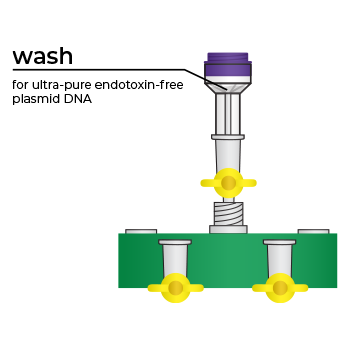
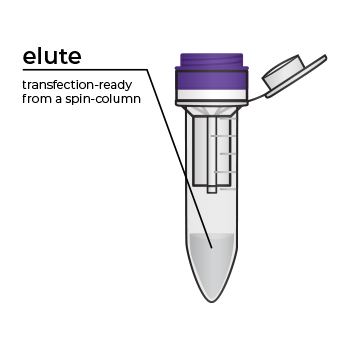
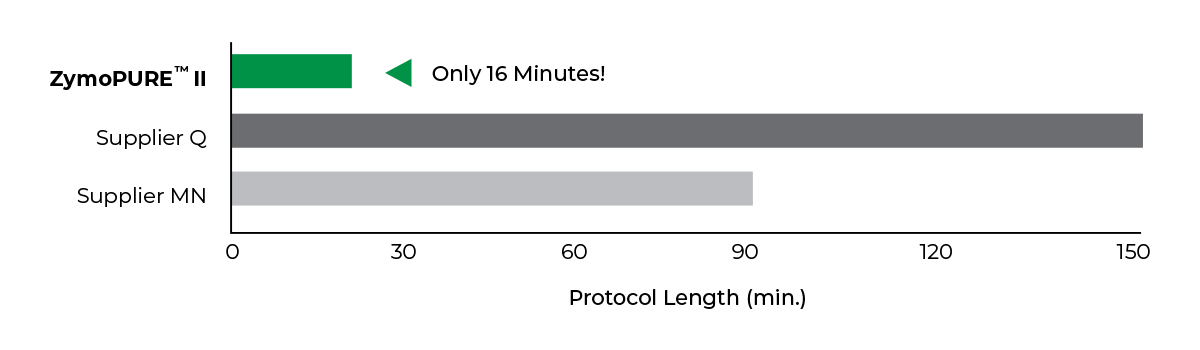
Simply bind, wash, and elute.
Simply bind, wash and elute. Novel binding chemistry and spin-column enables simple purification of transfection-ready plasmid DNA up to 9x faster using a vacuum manifold or centrifuge. No slow gravity flow columns, no tedious alcohol precipitation.
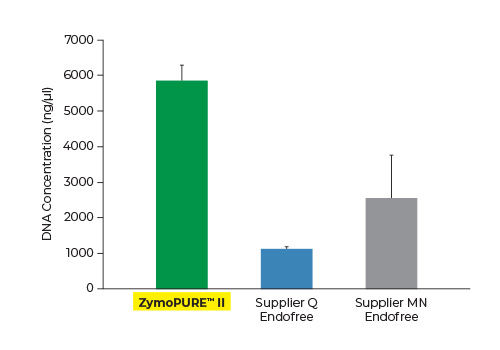
Highest Yield. Lowest Elution Volume.
Up to 6x More Concentrated Plasmid
Up to 3x More Plasmid DNA Yield
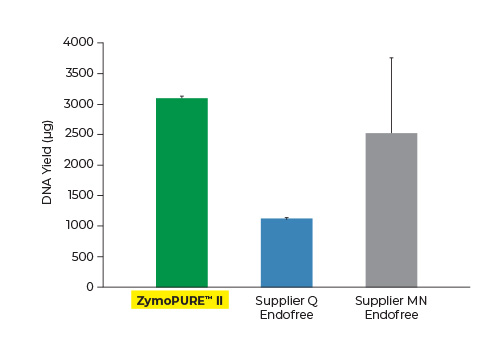
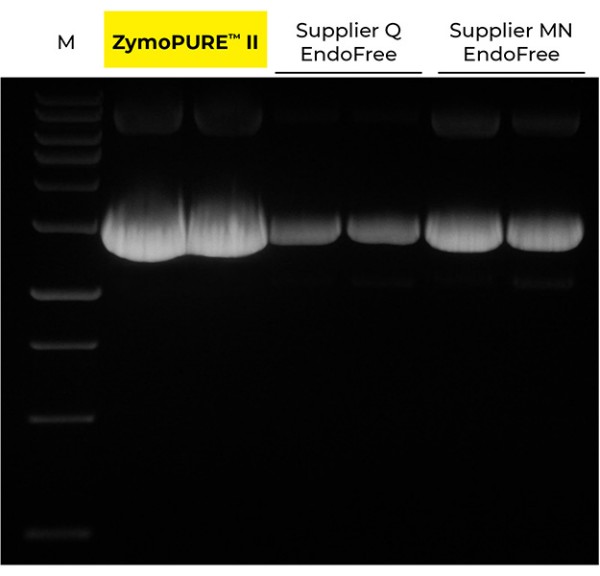
Yield and concentration for plasmid DNA isolated using the ZymoPURE II Maxiprep kit compared to two endotoxin-free plasmid purification kits from Supplier Q and Supplier MN. Plasmid DNA (pGL3®) was isolated from 150 ml of JM109 E. coli culture grown overnight following the manufacturer’s suggested protocol (in duplicate). One (1) µl of eluted plasmid DNA was visualized post agarose gel electrophoresis. M, ZR 1 kb DNA Marker (Zymo Research).
Transfection Ready Plasmid DNA

Endotoxin-Free
Purify Endotoxin-Free Plasmid with ZymoPURE II Midi, Maxi & Gigaprep Kits

Application-ready
CRISPR, gene modification, lentiviral vectors, synthetic biology, etc.
Ultra-Pure
For sensitive primary cells, in vivo injections, cloning, etc.
Superior Transfection Efficiency
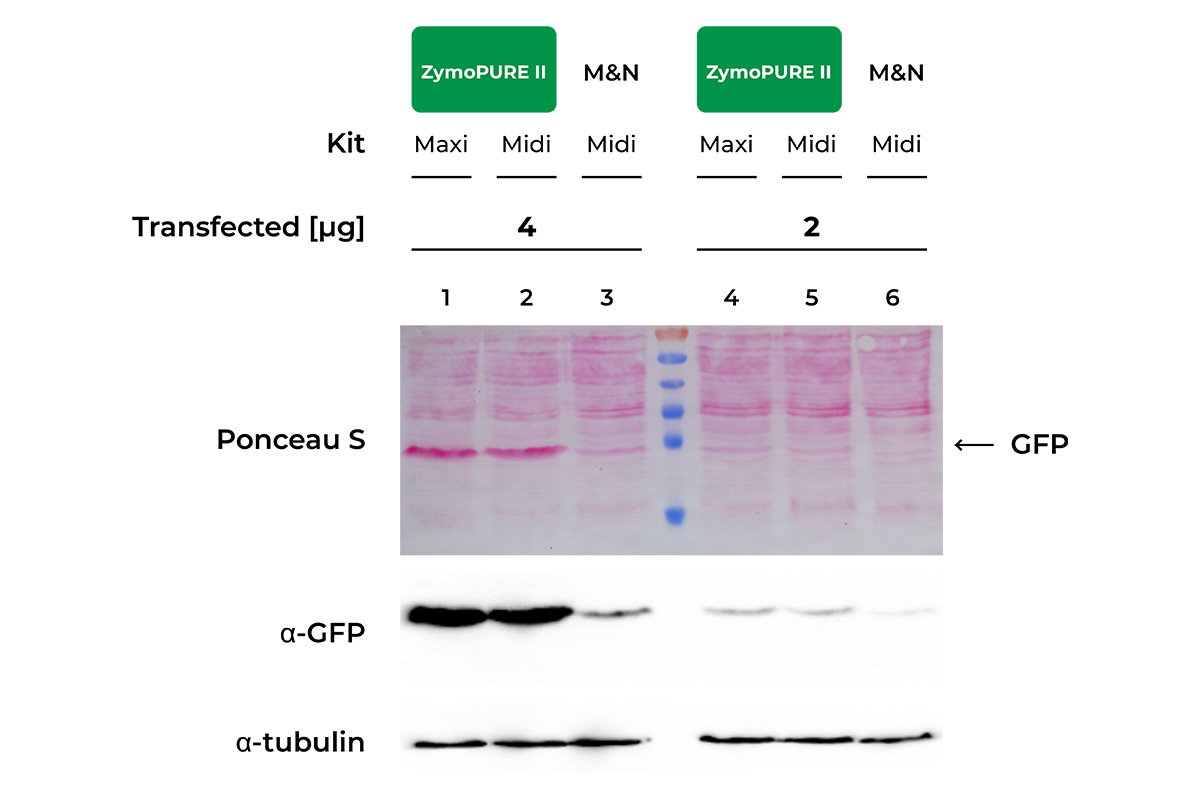
HeLa Cells seeded in a 6-well plate were transfected with either 2 or 4 µg of pCI-neo®+GFP plasmid isolated from 100 ml of bacteria culture using the ZymoPURE Midiprep Kit, ZymoPURE Maxiprep Kit, or MN Midiprep Kit. GFP expressin was assessed 48 hours later in cell lysates using western blot and Ponceau S staining. The blot was also probed with an antibody against alpha-Tubulin in order to verify equal loading samples.
Data generated by V.B. at University of Cologne
Unrivaled Technology
*Manufacturer's stated maximum yield
**Defined as < 0.1 EU/µg of plasmid DNA
ZymoPURE endotoxin-free plasmid purification kits are the fastest and simplest plasmid purification methods available to efficiently isolate a high yield of transfection-grade plasmid DNA from E. coli in as little as 16 minutes. Plasmid DNA is endotoxin-free and ready for immediate use in downstream applications such as transfection, in vivo injections, in vitro transcription, molecular cloning, PCR, and many more.
Cited for Sensitive Applications
Cell Therapy | Gene Therapy | Protein Replacement Therapy |
Recombinant Antibody Therapy |
Vaccine Development |
CAR T-Cell Therapy/Immunotherapy | Transfection |
Gene Editing |
Viral Vector Production (Lentivirus/Adenovirus/AAV) |
In vitro transcription/translation |
Transgenic organism generation | Microinjection of embryos |
and more…
ZymoPURE Plasmid Purification Kits
The ZymoPURE family of plasmid purification kit formats handle different amounts of culture input, ranging from miniprep (≤ 5 ml), midiprep (≤ 50 ml), maxiprep (≤ 150 ml) and gigaprep (≤ 2.5 L).
Endotoxin-Free Plasmid Purification Kits
Uses for Endotoxin-Free Plasmid Purification Kits
Use endotoxin-free plasmid purification kits to remove contaminating endotoxins during the extraction of plasmid DNA from E. coli. Endotoxins, also known as lipopolysaccharides or LPS, are a component of the cell membrane of most gram-negative bacteria. This molecule serves a practical purpose for the bacteria as it helps preserve the integrity of the cell wall and maintains a charge differential across the membrane that stabilizes the bacteria. LPSs are so integral to cell survival that the lack of it will effectively kill the cell, preventing its removal in all but a few strains of bacteria. Due to its ubiquity in gram-negative bacteria, most eukaryotic immune systems recognize endotoxins and will respond with a strong immune response. Additionally, because of the chemical structure of LPS and its tendency to form micelles, it often copurifies with DNA during traditional plasmid preparation workflows. Consequently, the presence of endotoxins in purified plasmid is a major issue for researchers working with mammalian systems, as it can significantly affect cell behavior, or even cause cell death, if introduced during transfection. Therefore, an endotoxin-free plasmid purification kit is necessary when preparing plasmid DNA for transfecting mammalian cells or tissues with plasmid DNA.
How is Endotoxin-Free Plasmid typically purified?
Traditionally, endotoxin-free plasmid was purified using Cesium Chloride (CsCl) density gradient centrifugation. However, this method requires the use of hazardous reagents and expensive ultracentrifuges. In addition, the density gradient centrifugation, phase separation, and alcohol precipitation steps are long and tedious to perform and prone to errors. Typically, a significant amount of DNA is lost during CsCl extraction. The process for purifying endotoxin-free plasmid DNA was later improved with the introduction of anion-exchange column-based endotoxin-free plasmid purification kits. These types of endotoxin-free plasmid purification kits dramatically reduced the time and number of steps it takes to prepare endotoxin-free plasmid DNA compared to CsCl density gradient centrifugation, but they typically still take several hours to perform because they rely on slow gravity flow columns to initially purify the plasmid DNA and multiple lengthy centrifugation steps to clean-up and concentrate the eluted plasmid DNA further.
We’ve pioneered rapid, efficient endotoxin-free plasmid purification kits with the introduction of our ZymoPURE Plasmid Purification product line. This family of plasmid purification kits feature a patented binding chemistry that enables simple purification of highly concentrated (up to 6 mg/ml) endotoxin-free plasmid DNA using a spin-column. The streamlined workflow eliminates slow gravity flow anion-exchange columns and isopropanol precipitation steps found in other kits. ZymoPURE plasmid purification kits reduce the time it takes to purify endotoxin-free plasmid by up to 9x using a vacuum manifold or centrifuge. Simply bind, wash, and elute transfection ready, endotoxin-free plasmid in minutes.
The ZymoPURE plasmid purification kits are optimized to ensure the eluted DNA is free of endotoxins, salt, protein, and RNA, resulting in plasmids that are suitable for use in sensitive applications. The resulting endotoxin-free plasmid DNA is ideal for transfection (including sensitive and primary cells), CRISPR-Cas9 and gene editing, lentiviral vectors, adenovirus vectors, AAV vectors, gene therapy, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) generation, recombinant antibody generation, in vitro transcription and translation, synthetic biology, PCR, transgenic organism generation and microinjections, molecular cloning, restriction endonuclease digestions, site-directed mutagenesis, plasmid transformation of competent cells, Sanger sequencing, and other sensitive downstream applications.
Do I Need an Endotoxin-Free Plasmid Purification Kit?
Both standard and endotoxin-free plasmid purification kits will prepare plasmid DNA from E. coli culture that is suitable for a variety of downstream applications. Endotoxins will not negatively affect many routine molecular biology techniques, such as transforming bacteria and yeast, DNA sequencing, PCR, restriction enzyme digestions, ligations, gibson assembly, and golden gate assembly, so an endotoxin-free plasmid purification kit is not always necessary. However, when introducing the plasmid into a biological system that is sensitive to endotoxins, such as mammalian cells or tissues, it is imperative that an endotoxin-free plasmid purification kit is used to prepare plasmid DNA that is low in endotoxins, so the experiment and results are not comprised. Also, not all standard plasmid purification kits are created equally, and some might be more prone to the carryover of other contaminants, such as salts, proteins, and RNA, which will also be detrimental to a variety of molecular biology techniques. Therefore, since endotoxin-free plasmid purification kits have typically been optimized to produce the highest-quality plasmid, they are generally the safest bet for preparing plasmid DNA for any sensitive downstream application.
Which Endotoxin-Free Plasmid Purification Kit is right for me?
There are a couple important points to consider when selecting an endotoxin-free plasmid purification kit. First, is the amount of overnight E. coli culture you want to process and the amount of plasmid DNA you are trying to prepare, which will generally be determined by your downstream transfection experiments (number of cells to transfect, transfection method, number of replicates, etc.). Our endotoxin-free plasmid purification kits are available in a variety of scales, including mini, midi, maxi, and giga preps. Therefore, you can process just a few milliliters of overnight culture to purify tens of micrograms of plasmid with a miniprep or liters of overnight culture to purify milligrams of plasmid DNA with a gigaprep. Second, is the level of endotoxins in the prepared plasmid DNA, which will largely be determined by the biological system that you are going to transfect. An endotoxin level in the purified plasmid of less than 50 endotoxin units per microgram of plasmid (< 50 EU/µg) will generally be sufficient for transfecting standard immortalized cell lines, such as HeLa, HEK293, and CHO. However, for primary cells, it is recommended to use plasmid that has less than 10 endotoxin units per microgram of plasmid (< 10 EU/µg) and 1 endotoxin unit per microgram of plasmid (≤ 1 EU/µg) for sensitive primary cells. For in vivo transfection and transfecting immune cells, it is recommended to use purified plasmid DNA that has less than 0.1 endotoxin units per microgram of plasmid (≤ 0.1 EU/µg). Zymo Research provides endotoxin-free plasmid purification kits that are sufficient for preparing plasmid DNA for even these most sensitive transfection experiments.
ZymoPURE Citations for Sensitive Applications
- Ramos-Murillo, Ana Isabel, et al. Efficient Non-Viral Gene Modification of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Umbilical Cord Wharton’s Jelly with Polyethylenimine. Pharmaceutics 12 9 896 2020.
- Vaughan, Hannah J, et al. Poly (beta-amino ester) nanoparticles enable tumor-specific TRAIL secretion and a bystander effect to treat liver cancer. Molecular Therapy-Oncolytics 21 377-388 2021.
- Lemmerman, Luke R, et al. Nanotransfection-based vasculogenic cell reprogramming drives functional recovery in a mouse model of ischemic stroke. Science Advances 712 eabd4735 2021.
- Gross, Tobias, et al. Characterization of CRISPR/Cas9 RANKL knockout mesenchymal stem cell clones based on single-cell printing technology and Emulsion Coupling assay as a low-cellularity workflow for single-cell cloning. Plos one 16 3 e0238330 2021.
- Tang, Shirley, et al. Nonviral Transfection With Brachyury Reprograms Human Intervertebral Disc Cells to a Pro‐Anabolic Anti‐Catabolic/ Inflammatory Phenotype: A Proof of Concept Study. Journal of Orthopaedic Research 37 11 2389-2400 2019.
- McMahon, Moira A, et al. Gene disruption using chemically modified CRISPR-Cpf1 RNA. CRISPR Guide RNA Design 49-60 2021.
- Zhang, Liyang, et al. AsCas12a ultra nuclease facilitates the rapid generation of therapeutic cell medicines. Nature Communications 12 1 44211 2021.
- Moore, Jordan T, et al. Nanochannel‐Based Poration Drives Benign and Effective Nonviral Gene Delivery to Peripheral Nerve Tissue. Advanced Biosystems 4 11 2000157 2020.
- Tang, S, et al. Non-viral reprogramming of human nucleus pulposus cells with FOXF1 via extracellular vesicle delivery: an in vitro and in vivo study. European Cells & Materials 41 90-107 2021.
- Chamberlain, Kyle, et al. A calsequestrin cis-regulatory motif coupled to a cardiac troponin T promoter improves cardiac adeno-associated virus serotype 9 transduction specificity. Human Gene Therapy 29 8 927-937 2018.
- Roy, Sashwati, et al. Neurogenic tissue nanotransfection in the management of cutaneous diabetic polyneuropathy. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine 2 102220 2020.
- Alzate-Correa, Diego, et al. Isolation and Nanoscale Electroporation of Primary Neuronal Cultures In Situ. Electroporation Protocols 145-152 2020.
- Li, Linxi, et al. Endogenously produced LG3/4/5-peptide protects testes against toxicant-induced injury. Cell Death & Disease 11 6 44215 2020.
- Yang, Xiao-Fei, et al. Direct reprogramming of hepatocytes into insulin-producing cells for anti-diabetic treatment by ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction enhanced hydrodynamic gene delivery. American Journal of Translational Research 12 11 7275 2020.
- Rodriguez, Juan A, et al. Ghrelin receptor agonist rescues excess neonatal mortality in a Prader-Willi syndrome mouse model. Endocrinology 159 12 4006-4022 2018.
- Gurramkonda, Chandrasekhar, et al. Improving the recombinant human erythropoietin glycosylation using microsome supplementation in CHO cell‐free system. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 115 51253-1264 2018.
- Tran, Kevin, et al. Cell‐free production of a therapeutic protein: Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant SK using a CHO lysate. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 115 1 92-102 2018.
- Hunter, Dominic JB, et al. Unexpected instabilities explain batch‐to‐batch variability in cell‐free protein expression systems. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 11581904-1914 2018.
- Peñalber‐Johnstone, Chariz, et al. Optimizing cell‐free protein expression in CHO: Assessing small molecule mass transfer effects in various reactor configurations. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 114 7 1478-1486 2017.
- Keating, Sheila M, et al. Generation of recombinant hyperimmune globulins from diverse B-cell repertoires. Nature Biotechnology 44207 2021.
- Vazquez-Lombardi, Rodrigo, et al. Transient expression of human antibodies in mammalian cells. Nature Protocols 13 1 99-117 2018.
- Nguyen, Annalee W, et al. Engineering Antibodies on the Surface of CHO Cells. Genotype Phenotype Coupling 397-422 2020.
- Wang, Chensu, et al. Reprogramming NK Cells and Macrophages via Combined Antibody and Cytokine Therapy Primes Tumors for Elimination by Checkpoint Blockade. CellPress Ahead of Print 2021.
- Adler, Adam S, et al. Rare, high-affinity anti-pathogen antibodies from human repertoires, discovered using microfluidics and molecular genomics. MAbs 9 8 1282-1296 2017.
- Vazquez-Lombardi, Rodrigo; et al. Expression of IgG Monoclonals with Engineered Immune Effector Functions. Antibody Engineering 313-334 2018.
- Piepenbrink, Michael S, et al. Therapeutic activity of an inhaled potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing human monoclonal antibody in hamsters. Cell Reports Medicine 2 3 100218 2021.
- Haabeth, Ole AW, et al. An mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine employing Charge-Altering Releasable Transporters with a TLR-9 agonist induces neutralizing antibodies and T cell memory. ACS Central Science 2021.
- Colluru, Viswa Teja, et al. Mini-intronic plasmid vaccination elicits tolerant LAG3+ CD8+ T cells and inferior antitumor responses. Oncoimmunology 5 10 e1223002 2016.
- Whitacre, DC, et al. Designing a therapeutic hepatitis B vaccine to circumvent immune tolerance. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics 16 2 251-268 2020.
- Kath, Jonas, et al. Fast, efficient and virus-free generation of TRAC-replaced CAR T cells. CellPress Ahead of Print 2021.
- Tsuji, Takemasa; et al. Rapid construction of antitumor T-cell receptor vectors from frozen tumors for engineered T-cell therapy. Cancer Immunology Research 6 5 594-604 2018.
- Shi, Xiaojing; et al. Genetically engineered cell-derived nanoparticles for targeted breast cancer immunotherapy. Molecular Therapy 28 2 536-547 2020.
- Duarte-Sanmiguel, Silvia, et al. Nanoelectroporation and Collection of Genetically Modified Exosomes in Primary Cultures of Dendritic Cells. Electroporation Protocols 79-84 2020.
- Cheng, Qinqin, et al. Reprogramming Exosomes for Immunotherapy. Cell Reprogramming for Immunotherapy 197-209 2020.
- Koblan, LW, et al., Improving cytidine and adenine base editors by expression optimization and ancestral reconstruction. Nature Biotechnology 843-846 2018.
- Findlay, GM, et al. Accurate classification of BRCA1 variants with saturation genome editing. Nature 562 217-222 2018.
- Hu, JH, et al. Evolved Cas9 variants with broad PAM compatibility and high DNA specificity. Nature 57-63 2018.
- Salasova, A, et al. A proteomic analysis of LRRK2 binding partners reveals interactions with multiple signaling components of the WNT/PCP pathway. Molecular Neurodegeneration 12 54 2017.
- Jaitin, D.A, et al. Dissecting immune circuits by linking CRISPR-Pooled Screens with Single-Cell RNA-Seq. Cell 1883-1896 2016.
- Marshall, R, et al. Rapid and Scalable Characterization of CRISPR Technologies Using an E. coli Cell-Free Transcription-Translation System. Molecular Cell 146-157 2017.
- Champer J, et al. Novel CRISPR/Cas9 gene drive constructs reveal insights into mechanisms of resistance allele formation and drive efficiency in genetically diverse populations. PLoS Genetics 13 7 2017.
- Aram, R, et al. Tools for Mos1-mediated single copy insertion (mosSCI) with excisable unc-119(+) or NeoR (G418) selection cassettes. microPublication Biology 2019.











