Successfully Added to Cart
Customers also bought...
-
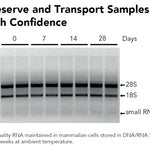 DNA/RNA Shield (50 ml)Cat#: R1100-50DNA/RNA Shield reagent is a DNA and RNA stabilization solution for nucleic acids in any biological sample. This DNA and RNA stabilization solution preserves the...
DNA/RNA Shield (50 ml)Cat#: R1100-50DNA/RNA Shield reagent is a DNA and RNA stabilization solution for nucleic acids in any biological sample. This DNA and RNA stabilization solution preserves the... -
 DNA/RNA Shield SafeCollect Swab Collection Kit (1 ml fill) (1 collection kit)Cat#: R1160The DNA/RNA Shield SafeCollect Swab Collection Kit is a user-friendly collection kit for stabilizing the nucleic acid content of samples collected with a swab. DNA/RNA...
DNA/RNA Shield SafeCollect Swab Collection Kit (1 ml fill) (1 collection kit)Cat#: R1160The DNA/RNA Shield SafeCollect Swab Collection Kit is a user-friendly collection kit for stabilizing the nucleic acid content of samples collected with a swab. DNA/RNA...
Highlights
- Innovative library preparation for strand-specific mapping of 5-hmC in DNA.
- Streamlined workflow accommodates low (≥100ng) DNA inputs.
- Libraries are ready for Next-Generation sequencing (Illumina-compatible).
Original Manufacturer
Satisfaction 100% guaranteed, read Our Promise
Innovated in California, Made in the USA
Highlights
- Innovative library preparation for strand-specific mapping of 5-hmC in DNA.
- Streamlined workflow accommodates low (≥100ng) DNA inputs.
- Libraries are ready for Next-Generation sequencing (Illumina-compatible).
Original Manufacturer
Satisfaction 100% guaranteed, read Our Promise
Innovated in California, Made in the USA
| Cat # | Name | Size | |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1000-1 | dNTP Mix [10 mM] | 100 µl | |
| E2050 | |||
| C1004-50 | Zymo-Spin IC Columns | 50 Pack | |
| C1001-50 | Collection Tubes | 50 Pack | |
| D3004-4-4 | DNA Elution Buffer | 4 ml | |
| W1001-1 | DNase/RNase-Free Water | 1 ml | |
| W1001-4 | DNase/RNase-Free Water | 4 ml | |
| D4003-1-25 | DNA Binding Buffer | 25 ml | |
| D4003-1-L | DNA Binding Buffer | 50 ml | |
| D4001-1-50 | ADB (Agarose Dissolving Buffer) | 50 ml | |
| D4003-2-24 | DNA Wash Buffer (Concentrate) | 24 ml | |
| D4003-2-6 | DNA Wash Buffer (Concentrate) | 6 ml | |
Description
Performance
Technical Specifications
| Equipment Required | Microcentrifuge, thermocycler with heated lid, and gel electrophoresis or other equipment for DNA visualization |
|---|---|
| Input | 100 ng - 1 µg |
| Sample Source | High quality, intact genomic DNA free of enzymatic inhibitors. |
| Sequencing Compatibility | Any Illumina sequencing platforms |
Resources
Documents
FAQ
RRHP is designed as a genome-wide 5hmC profiling method, meaning 5hmC can be analyzed across the whole genome. Your region of interest may or may not be covered depending on (1) whether your region falls within the MspI digested fragments and (2) whether your regions contain 5hmC. For region specific analysis, we offer the Quest 5hmC Detection Kit (D5410), which is a restriction-enzyme qPCR method that can target your desired regions.
-Make sure you are using the recommended DNA input based on your sample type. -The glucosylation reaction should be carried out for a minimum of 2 hours, and, for the final MspI digestion, it is best to let it digest overnight (i.e. > 8 hours).
Yes, the index primers provided in both kits are the same. Both kits use the primer sequences off the Illumina TruSeq Small RNA Library Prep Kits.
Any standard trimming and alignment program are suitable. The default quality trimming parameters for Illumina TruSeq adapters can be used. After reads are aligned to the genome of interest, reads containing the 5’-CCGG tag can be counted to determine relative 5hmC levels.
RRHP libraries are compatible with any Illumina instruments, and they can be sequenced using the default settings. Usually, 50 base single-end reads are sufficient for alignment and analysis, as RRHP rely only on reads that begin with the “CCGG” tags, which only appears during Read 1. However, paired-end reads can help improve the mapping specificity, but may require some trimming for shorter inserts. Since RRHP has low-diversity during the first five bases, we recommend spiking-in a minimum of 10% PhiX to increase the diversity and improve sequencing quality.
RRHP is a positive-display method, so the amount of amplification is related to the level of 5-hmC present in your sample. If you are processing samples that have very low 5hmC% (e.g. spleen), there is less template available to amplify. Here are some guidelines and considerations for ensuring optimal library yield: 1. Increase the number of amplification cycles by increments of 2. 2. For samples with low 5hmC%, we recommend using a starting input of 500 ng. 3. Be sure that you are using high-quality, intact genomic DNA from the start. 4. Check that genomic DNA has been accurately quantified (no RNA contamination). 5. Ensure that the wash buffer has the appropriate amount of ethanol added. 6. Ensure that the agarose gel has dissolved completely before proceeding to purification.
The index primers provided in the kit contain the forward and reverse primers at 10 µM each.
Any system that utilizes the TruSeq LT adapters is compatible with RRHP library preparation kit. The full sequences of Illumina TruSeq adapters and indices are available on Illumina’s website.
Additional oligos with different index sequences can be synthesized if >6 sample multiplexing is required. The reverse complement of the published Illumina sequence should be ordered for the final library amplification.
Yes, beads are suitable; anything lower than 100 bp should be removed to prevent adapter dimers in the final library product.
For best results, the MspI can be left to digest overnight (8 hours).
The reaction has been shown to be complete after a 2 h incubation, but longer incubation does not affect the library preparation.
It is not necessary to inactivate MspI as it does not have star activity.
It is highly dependent on your sample type and whether it has an overall high 5-hmC level. The minimum DNA input for neuronal DNA is 100 ng and 500 ng for non-neuronal DNA.
The RRHP library preparation kit only allows for 5-hmC analysis. However, the methodology can be adapted to look at methylation, if desired. Please contact Zymo Research Technical Support and we can provide additional guidance if you would like to look at 5-mC as well.
RRHP is a semi-quantitative method as the level of 5hmC is deduced based on the number of sequencing reads a particular CCGG site receives (i.e. higher reads are correlated with higher 5hmC level). TAB-seq and oxBS-seq are quantitative methods in which you will determine the 5hmC%. However, these methods rely on bisulfite conversion and require higher sequencing depth. OxBS-seq requires double the amount of sequencing as it requires subtractive sequencing to determine the 5hmC%.
Yes, but we cannot guarantee the same performance. Some polymerases show bias in amplifying unmodified over modified DNA (addition of glucose to the 5-hmC site creates a bulky group that can stall certain polymerases).
Citations
Characterization of midbrain dopaminergic neurons is important for understanding Parkinson’s disease, but identifying and purifying induced dopaminergic (iDA) neurons from a heterogeneous cell population can be difficult. Therefore, the authors generated an embryonic stem cell line with a tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-RFP reporter to selectively purify iDA neurons, enabling precise transcriptional and epigenetics analysis. The 5-hydroxymethylation patterns profiled using the RRHP kit were compared to identified enhancer regions and RNA-seq data. The analysis revealed dozens of transcription factors, including homeobox TF UNCX and other well-known dopaminergic neuron regulators, that may be important for induction and maintenance of dopaminergic neurons.
Xia N, et. al. (2017) A Knockin Reporter Allows Purification and Characterization of mDA Neurons from Heterogeneous Populations. Cell Reports 18(10)2533-2546.Need help? Contact Us